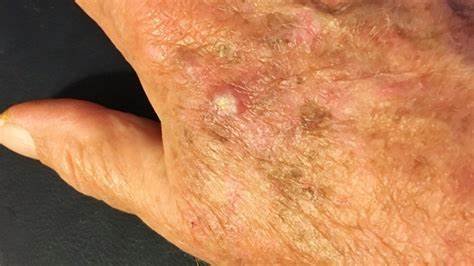
Actinic keratosis (AK), also known as solar keratosis or senile keratosis, is a precancerous skin condition caused by prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) rays, usually from the sun. It manifests as scaly, rough patches on the skin and has the potential to progress to squamous cell carcinoma if left untreated.
Causes of Actinic Keratosis:
Sun Exposure:
Chronic exposure to sunlight, especially in individuals with fair skin, is the primary cause of actinic keratosis.
Artificial UV Radiation:
Tanning beds and other sources of artificial UV radiation can also contribute to the development of actinic keratosis.
Age:
Actinic keratosis is more common in older adults, as cumulative sun exposure over time increases the risk.
Weakened Immune System:
Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those with organ transplants or certain medical conditions, are at a higher risk.
Fair Skin and Light Eyes:
People with fair skin, light-colored eyes, and blonde or red hair are more susceptible to actinic keratosis.
Geographic Location:
Living in areas with high levels of sunlight, such as sunny climates or at high altitudes, increases the risk.
Symptoms of Actinic Keratosis:
Rough, Scaly Patches:
Actinic keratosis typically presents as dry, scaly, or rough patches on sun-exposed areas of the skin. You can visit a Dermatologist in Karachi for medical assistance.
Color Changes:
The patches can range in color from pink to red or brown and may have a white or yellowish scale.
Itching or Burning Sensation:
Some individuals may experience itching or a burning sensation in the affected areas.
Hard, Horn-Like Bumps:
In more advanced cases, actinic keratosis may progress to the development of hard, horn-like bumps.
Treatment of Actinic Keratosis:
Topical Medications:
Prescription creams or gels containing ingredients like imiquimod, diclofenac, or fluorouracil can help eliminate actinic keratosis lesions.
Cryotherapy:
Liquid nitrogen is applied to freeze and destroy the abnormal cells.
Photodynamic Therapy:
A combination of a light-sensitizing medication and light exposure is used to target and destroy actinic keratosis cells.
Laser Therapy:
Lasers can be used to selectively target and remove actinic keratosis lesions.
Curettage and Electrosurgery:
Scraping off the lesion with a curette followed by electrosurgery can be an effective treatment.
Chemical Peels:
Application of a chemical solution to the skin causes peeling and removal of the damaged cells.
Preventive Measures:
Sun protection measures, such as using sunscreen, wearing protective clothing, and avoiding excessive sun exposure, can help prevent the development of new lesions.
It’s important for individuals with actinic keratosis to seek medical attention, as untreated lesions can progress to squamous cell carcinoma. Regular skin checks and early intervention are crucial for managing actinic keratosis and reducing the risk of skin cancer. Individuals with a history of actinic keratosis should also have regular dermatologic evaluations. Book an appointment with a Dermatologist in Lahore for further evaluation.