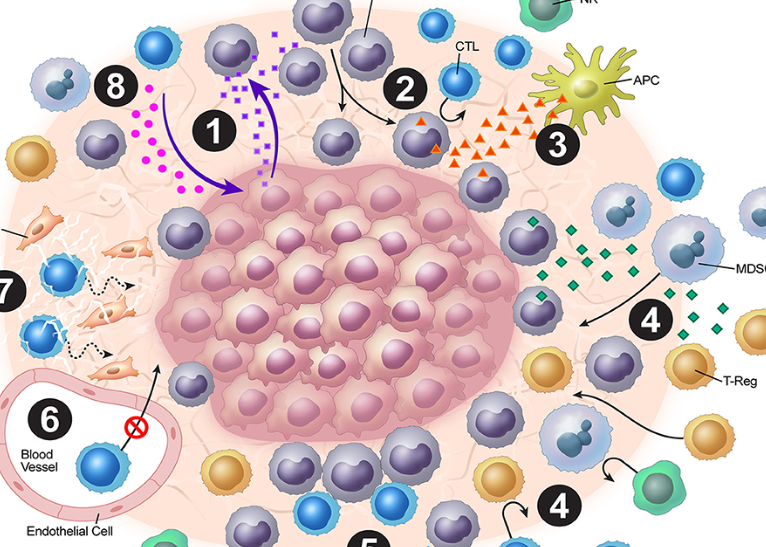
The tumor stroma also known as the Tumor microenvironment, is a complex network of cells and proteins that promotes the growth and dissemination of malignant cells. It is composed of numerous cell types and extracellular matrix components, and it plays a crucial role in the progression and development of cancer. This article will discuss the significance of Tumor stroma, its constituents, and how they contribute to the development and spread of cancer
Immune cells, fibroblasts, and endothelial cells are present within the Tumor microenvironment, among others. These cells can interact and produce cytokines, chemokines, and growth factors that promote Tumor cell growth. In addition, the extracellular matrix provides Tumor cells with structural support and facilitates their adhesion to the adjacent tissue.
The Tumor microenvironment also contributes to the metastatic spread of cancer cells. The cells of the Tumor stroma are capable of producing proteases that degrade the extracellular matrix, thereby facilitating the migration and invasion of Tumor cells. This process, known as ” Tumor cell invasion,” is a crucial factor in the progression of cancer.
In addition to facilitating in cancer’s proliferation, the Tumor stroma can also influence Tumor growth. The Tumor microenvironment can provide a favourable environment for the proliferation and growth of Tumor cells. In addition, the Tumor stroma can generate growth factors that stimulate cell division and angiogenesis (the formation of new blood vessels).
Given the significance of the Tumor microenvironment in the development and progression of cancer, scientists have been investigating therapeutic approaches that target it. Drugs that target the Tumor stroma, such as anti-angiogenic compounds, can inhibit the growth and spread of cancer, for instance. Immunotherapies, such as checkpoint inhibitors, can also assist the immune system in recognising and attacking Tumor cells.
In conclusion, Tumor stroma is a complex network of cells and proteins that promotes the growth and spread of malignant cells. It is composed of numerous cell types and extracellular matrix components, and it plays a crucial role in the progression and development of cancer. By comprehending the function of Tumor stroma, researchers can develop more effective anti-cancer treatments.